Choicy aesthetic machine manufacturer provide Fractional COâ‚‚ Laser Therapy Machine,Medical Fractional COâ‚‚ Laser Machine,Fractional COâ‚‚ Laser for beauty salon. This fractional co2 laser machine can treat acne, spots, such as melasma, freckles, mole, surgery, and vaginal treatment. The dermatology co2 laser equips with two cutting tips, and a scanning head. It is widely used in dermatologists, doctors, etc. We encourage you to make get hold of, as we've been wanting for companions inside our venture. We are sure you'll uncover doing company with us not only fruitful, but also profitable. We've been prepared to provide you with what you require.
To view the full range of laser machines that we have available, you are welcome to contact us to have a video online meeting to see the machines up close and personal. Also, please send your requirements with a detailed list including the style/item and quantity you require. We will then send our best prices to you. Manufacturers Machine Operation training is included with all machines and no previous experience is required.
Application area
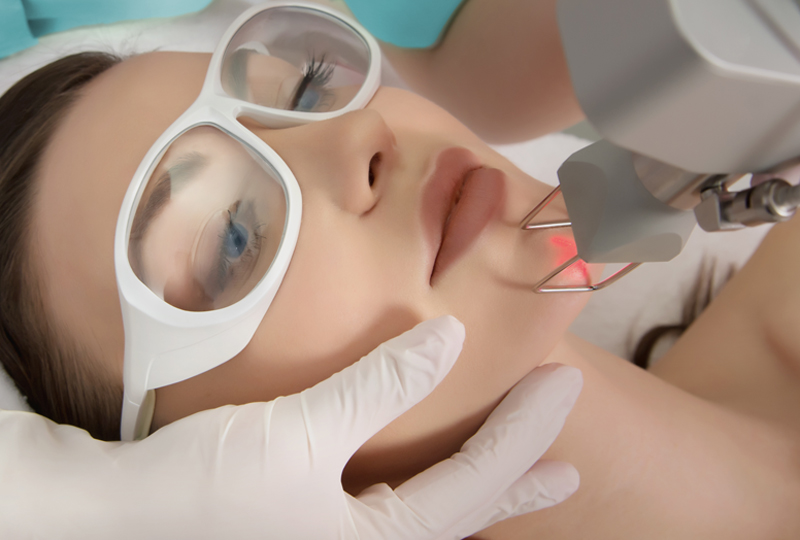
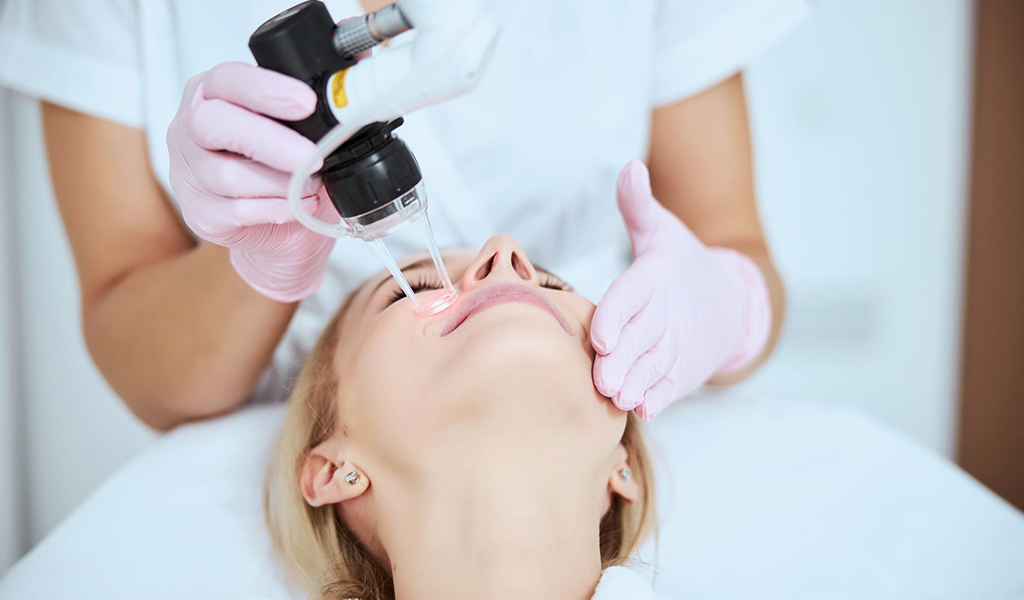
Dermatology Center
Medical Clinic
Co2 Fractional Laser Machine,Fractional Co2 Laser Machine,Medical Co2 Laser,Laser Co2 Fractional
Choicy , https://www.choicygroup.com