★Chemical information
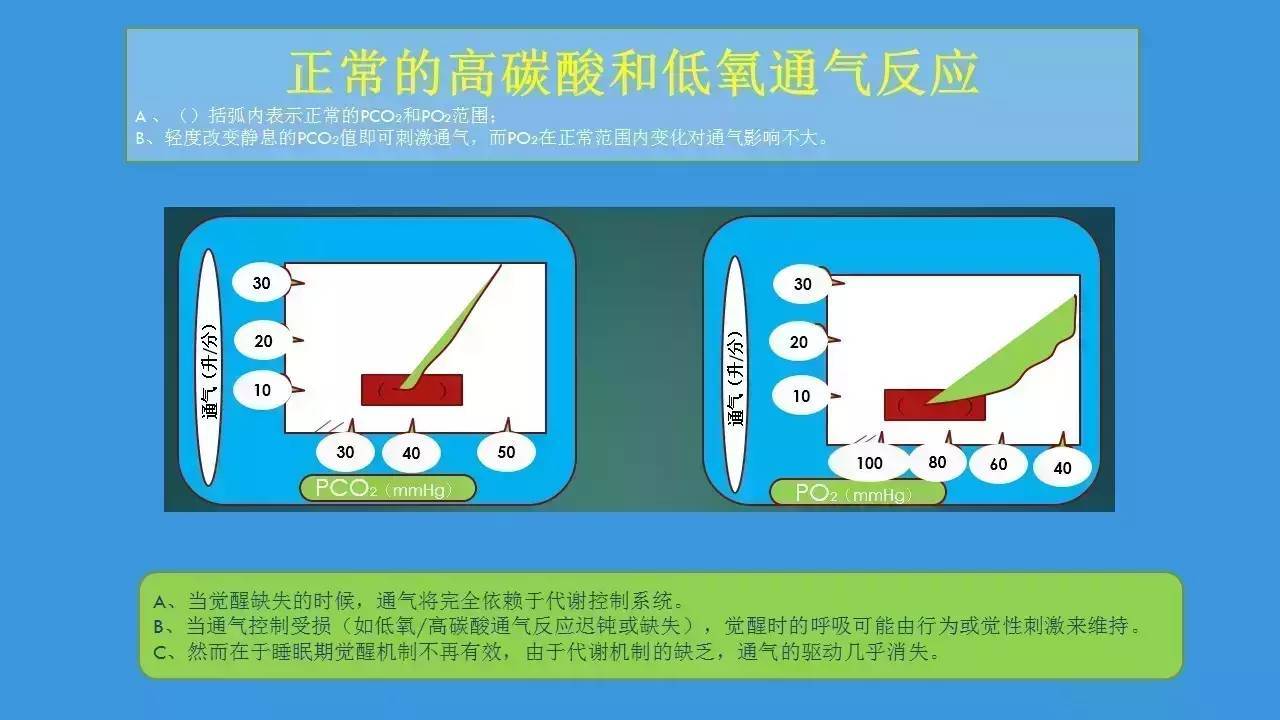
Carotid artery sensation--arterial blood oxygen PaO2--excepting excitatory central chemical impulse through the glossopharyngeal nerve to the medulla; when the PaO2 is lower than 60mmHg, the ventilation is enhanced;
When less than 40mmHg, hypoxemia occurred in the body, and the medullary respiratory center was inhibited, resulting in decreased ventilation; both carotid body and medullary receptors could sense arterial blood PaCO2, and when PaCO2 increased, the ventilation level increased linearly;
Drugs that inhibit the central nervous system can severely inhibit the chemical motility of breathing.
★Mechanical information
When the load of lung disease or respiratory system changes - the phase changes shortly during inhalation, the tidal volume becomes smaller, and a shallow breathing pattern occurs.
★Information from the advanced central nervous system
The respiratory system can perform non-respiratory functions under the command of a high-level nerve center, such as singing, laughing, crying, speech, etc., and the outgoing pathway can bypass the medullary respiratory center and does not have the function of maintaining metabolic stability of the respiratory control system;
Awakening itself is a kind of breathing power.
★Sleep ventilation control physiology
Hypoxic ventilatory response during sleep ------------ ventilation ↓ (REM <NREM <WAKE);
Hypercapnia ventilatory response during sleep ------- ventilation ↓ (REM <NREMII <NREMIII <WAKE);
Ventilation response caused by chemical stimulation - - - Conclusion (REM period is reduced to a minimum)
★ Increased airway resistance during sleep, increased obstruction
(airway resistance ↑)
★ Awakening reaction
Hypoxia at normal carbon dioxide levels - causing arousal stimulation is weak;
Hypercapnia---causing awakening reaction, when the end of PaCO2 is 15mmHg more than the awakening period, most of them can be awakened;
Increased airway resistance - increased resistance or blockage is prone to wakefulness, REM phase is more sensitive to NREM period;
Stimulation of the bronchus---the sleep period inhibits the cough response caused by inhalation stimulation;
Ventilation response caused by arousal - consistent with the reduction in ventilation at the beginning of sleep.
★ Control of sleep breathing rhythm
Hypocapnia combined with hypoxemia can induce irregular breathing in the NREM phase, which can further cause OSA; when the inspiratory resistance increases, the phenomenon is more obvious;
Hyperventilation - airway obstruction in the NREM phase may cause hyperventilation, resulting in unstable breathing;
Irregular respiration is common in adult REM sleep, and hypoxia or hypercapnia at normal CO2 levels cannot regulate breathing patterns to make them regular.
★ upper airway muscles open during sleep
The upper airway dilatation muscle activity is weakened, and the REM phase is more significant;
The tension of the sacral muscles and the genioglossus during sleep does not increase with the adaptability of airway resistance.
★Influencing factors of respiratory control during sleep
Decreased basal metabolic rate---the ventilatory and ventilatory responses are weakened when the basal metabolism declines, which may be the reason for the sensitivity of the sleep center to chemical stimuli;
Relationship between cerebral blood flow and metabolism---sleep period, increased cerebral blood flow;
Changes in the nervous system during sleep - cortical activity can affect breathing, and when ventilation is focused, ventilation and ventilation responses increase accordingly;
The activity of medullary respiratory neurons in REM sleep was positively correlated with the activity of POG waves generated by pons;
Neuromechanical factors---reduction of REM sleep ventilatory response is the result of weakened intercostal muscle tone;
Mechanism of reduced ventilation response - - - Conclusion
The NREM sleep ventilatory response is decreased, which is the cause of the decrease in respiratory motility, and the decrease in metabolism and the increase in airflow resistance are involved;
The REM sleep ventilatory response is further attenuated and may be the result of changes in central nervous system function.
★The clinical impact of abnormal ventilation response
Decreased ventilation response leads to insufficient sleep ventilation, causing sleep-related hypoxemia worsening in hypoxic chronic bronchitis and emphysema and other respiratory diseases that cause hypoxia, resulting in significant hypoxia before awakening in these patients And hypercapnia;
Unstable ventilation control may aggravate the condition of patients with OSAHS. Some patients may have increased ventilatory response and cause periodic breathing, which may be an important cause of Chen-spiring in patients with left ventricular failure.
Rapid Fill Water Ball is made for children to have fun with water balloon . The material is PET and different color can be offered . Rapid Fill Water Ball has a capacity from 250 ML to 2 L . Rapid Fill Water Ball has better quality and better drainage . We have many advantages over other products , first of all , we are very stricted in controling over the raw materials , sencondly , we have more than 20 years experience in mold translation . thirdly , we will carry out a complete inspection of each product , we have a complete set of testing equipment to ensure that each product to the hands of customers have no quality problems . We have many advantages over other products . Front switch is more easy to control , stepless can be adjusted . Rapid Fill Water Ball is very fun to be used . Children can fill up the ball with water quickly and safely.Rapid Fill Water Ball is really a good gift for children.
Rapid Fill Water Ball,Water Balloons,Rapid Fill Water Balloons,Quick Fill Water Balloon
YUYAO ZHENGYU SPRAYER FACTORY , https://www.zysprayer.com