Cell structure is an important research field in additive manufacturing . Just like hollow bricks for construction, the application of cells reduces the use of materials and effectively helps to achieve lightweight, while at the same time, how to ensure that the mechanical properties are still met. , it has become a matter of urgency in the modeling world, "only under the brow, but on the heart."
In this issue, Xiaobian and friends share several common structures and the application characteristics of these structures.
Four common structures
honeycomb
The honeycomb structure is the basic structure of the honeycomb, and is a structure in which a single hexagonal single room, the entire mouth of the room is facing downward or sideways, and the back-to-back is symmetrically arranged. This structure has excellent geometric mechanical properties and is therefore widely used in materials science.
Honeybee's honeycomb structure is very compact, suitable and saves material. The hive consists of countless rooms of the same size. The holes are all hexagonal. Each hole is surrounded by other holes. There is only one wax wall between the two holes. Surprisingly, the bottom of the hole is neither flat nor round, but pointed. This bottom is made up of three identical diamonds. Some people have measured the angle of the diamond, both obtuse angles are 109 ° and both acute angles are 70 °. What is amazing is that the honeycombs of all bees in the world are built according to this unified angle and mode.
The structure of the hive has aroused great interest among scientists. After an in-depth study of the hive, the scientists were surprised to find that the adjacent holes share a wall and a hole bottom, which saves building materials; the hole is a regular hexagon, the body of the bee is basically cylindrical, and the bee is There is no extra space in the room and no congestion. The structure of the honeycomb is a great inspiration for spacecraft designers. They used a honeycomb structure: they were made of metal into a honeycomb, and then they were clamped together with two metal plates to form a honeycomb structure. This honeycomb structure is high in strength and light in weight, and is also good for sound insulation and heat insulation. Therefore, today's space shuttles, satellites, and spacecraft use a large number of honeycomb structures inside, and the outer shells of satellites are almost all honeycomb structures. Therefore, these spacecraft are collectively referred to as "cellular spacecraft."
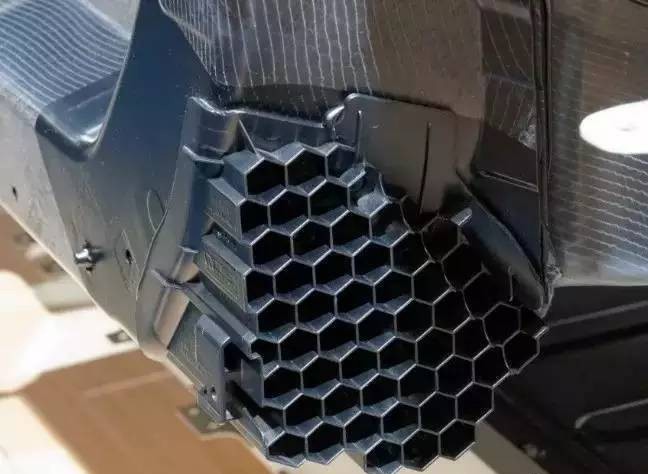

Figure: BMW i3 collision structure design part
Open cell foam
Most of the cells contained are foamed plastics that are connected to each other. The open-cell structure is obtained only when the following conditions are met: (1) each spherical or polygonal cell must have at least two holes or two failure faces; (2) most cell edges must be common to at least 3 structural units. .
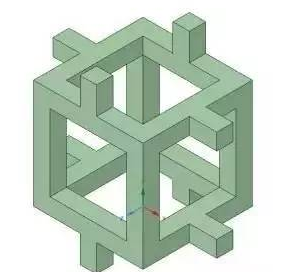
Compared to closed-cell foams, open-cell foams have a higher absorption capacity for water and moisture, higher permeability to gases and vapors, lower insulation for heat or electricity, and better absorption. And the ability to dampen sounds.
In terms of design impact, unlike honeycombs, open-cell foams are more suitable for stimulating environments (stress, flow, heat), which are unpredictable. As a "living tool" for absorbing energy, open-cell foams are suitable for use in complex structures. Interconnection between the open cell foam materials also allows fluid to flow through the structure more smoothly.
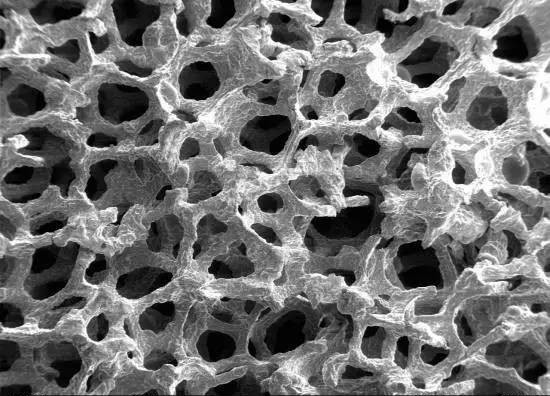
Figure: SEM image of metal foam
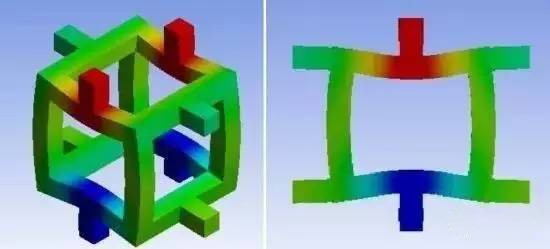
Figure: Finite element simulation of open-cell foam unit under compression, taking into account the main deformation modes of bending
Closed cell foam
The cells of the closed-cell foam are closed structures of the bubble wall and the bubble-environment, and the structure is complete, and the cells are mutually encouraged and mutually incompatible. However, in practice, the open-cell structure and the closed-cell structure may appear in the same foam, but the probability of occurrence is different. Therefore, according to the ratio of the open-cell structure and the closed-cell structure in the foam, a foam having a closed-cell structure of more than 90% is defined as a closed-cell foam; otherwise, it is defined as an open-cell foam.
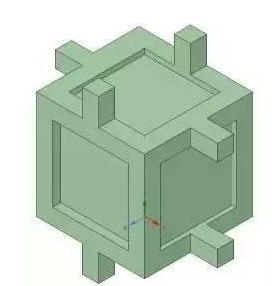
The cell structure has a significant impact on the properties of the foam. Under normal circumstances, the closed-cell foam has higher mechanical strength, superior thermal insulation and mitigation, and less water absorption, while the open-cell foam is softer and more Flexible and soundproof. In addition to the general foam properties, closed cell foams have lower thermal conductivity and water absorption.
Closed cell foams are commonly used for insulation, insulation, sound insulation, packaging, floatation, shock absorption, and structural materials.
Lattice
The appearance of the lattice is very similar to that of open-cell foam, but the difference is that the deformation of the lattice members is predominantly stretched rather than curved.
The material characteristics of the lattice structure are light weight, high strength ratio and high specific rigidity. It also brings a variety of thermodynamic features, and the ultra-lightweight structure of the lattice structure is suitable for use in impact/explosion systems, or as a heat sink, acoustic vibration, microwave absorbing structure, and drive system.
Boeing uses ultra-light 3D printed materials in lattice construction for non-mechanical components such as aircraft walls and floors. This greatly reduces the weight of the aircraft and improves the fuel efficiency of the aircraft. Thanks to the unique properties of the lattice structure and the low volumetric capacity, the combination of lattice structure and functional design has proven to be an area of ​​advantage for additive manufacturing.

Thales Alenia Space also printed a lattice-containing metal structure weighing 1.7 kg and a volume of 134 x 28 x 500 mm. Used on satellites in Thales Alenia Space, Europe's largest satellite manufacturer.
References recommended:
[1] Ashby, “Materials Selection in Mechanical Design,†Fourth Edition
[2] Gibson & Ashby, "Cellular Solids: Structure & Properties," Second Edition
[3] Gibson, Ashby & Harley, “Cellular Materials in Nature & Medicine,†First Edition
[4] Ashby, Evans, Fleck, Gibson, Hutchinson, Wadley, “Metal Foams: A Design Guide,†First Edition
[5] Deshpande, Ashby, Fleck, “Foam Topology Bending versus Stretching Dominated Architectures,†Acta Materialia 49
[6] Deshpande, Fleck, Ashby, “Effective properties of the octet-truss lattice material,†Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 49
High Gloss Buffet Cabinet,Kitchen Side Cupboard,Black Wood Dining Table,Kitchen And Dining Furniture Sets
Foshan Chengda Furniture Co.,ltd , https://www.catalogfur.com